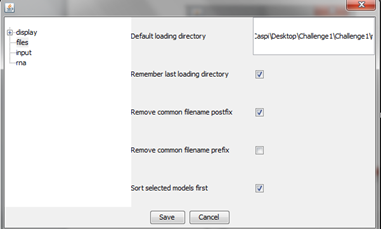
Main screen
Main screen of RNAlyzer

- A – Upper menu
- B – Graph menu
- C – Visualization area
- D – Models menu
- E – Operational menu
Multi-model plot
An example of Multi-model plot is presented in Figure 1. This is a multiple model line plot, where each line describes a single model analyzed. Each model is shown in a different color. RMSD values between atoms from the reference structure and corresponding atoms from the model analyzed are calculated for atoms included in the sphere, where the center of the sphere is a selected atom (predefined by the user). Spheres are built for every nucleotide in the considered reference structure.
The Multi-model plot visualizes how accurate is the prediction of atoms located in the neighborhood of every nucleotide, taking into consideration the sphere radius (each line describes exactly one structural model - different colors correspond to different models). With a low radius (small local neighborhood – high precision of assessment), the local quality of models analyzed is very good for almost all nucleotide residues in the model, because accurate modeling of chemical structures of nucleotide residues is relatively easy. With the increasing value of radius one can easily identify the parts of models that exhibit different accuracies of prediction, from low values of RMSD that indicate correct predictions, to important structural errors (for example different torsion angles – high values of RMSD for local neighborhood) that should be widely and carefully analyzed. If the radius increases to match the molecule radius (i.e. at the very low level of precision of assessment), RMSD value for the sphere that contains all nucleotides levels off to the same value, equal to global RMSD for a particular model (Fig. 1E).
The main feature of the Multi-model plot is Y-axis scaling of all predicted models to the potentially worst model, because its RMSD values are the highest. Visualization of two prediction models that differ significantly (one model – very good quality of prediction, second model – significant structural errors) on the Multi-model plot can be confusing because the RMSD value for the worse model may dominate the visualization of errors for the model with a better accuracy. Hence, the user can analyze each model separately.

Figure 1. Multi-model plot for Challenge_3 of RNApuzzless contest; each plot (A-E) represents results for a different sphere radius (3, 8, 20, 38, and 300 Å). X-axis represents the order of nucleotides in the sequence, Y- axis represents the value of RMSD.
RMSD averaged plot
An example of RMSD averaged plot is shown in Figure 2. This is also a multiple model line plot, where each line describes exactly one structural model (different colors correspond to different models). The difference between Multi-model plot and RMSD averaged plot is that in the latter case the Y-axis represents values of RMSD calculated as the averaged sum of RMSD of spheres built with fixed radius for all nucleotides of the analyzed RNA molecule. This plot visualizes how averaged RMSD values change with an increasing sphere radius. In general, this plot describes the changes of quality of prediction from the local structural neighborhood to the whole molecule point of view.

Figure 2. RMSD averaged plot; X-axis represents the sphere radius, Y-axis represents averaged RMSD for all spheres with fixed radius (different colors correspond to different models).
2D map plot
An example of a 2D map plot is presented in Figure 3. This plot visualizes exactly one model at a time. The values of RMSD are represented with a colored scale - RMSD values correspond to colors from blue (high prediction quality) to red (low prediction quality). The X-axis represents residue numbers (in sequential order), and the Y-axis represents the radius values from the spheres radii vector defined by the user. This plot shows where the prediction is inaccurate and allows the user to check if prediction errors are similar for different structures.
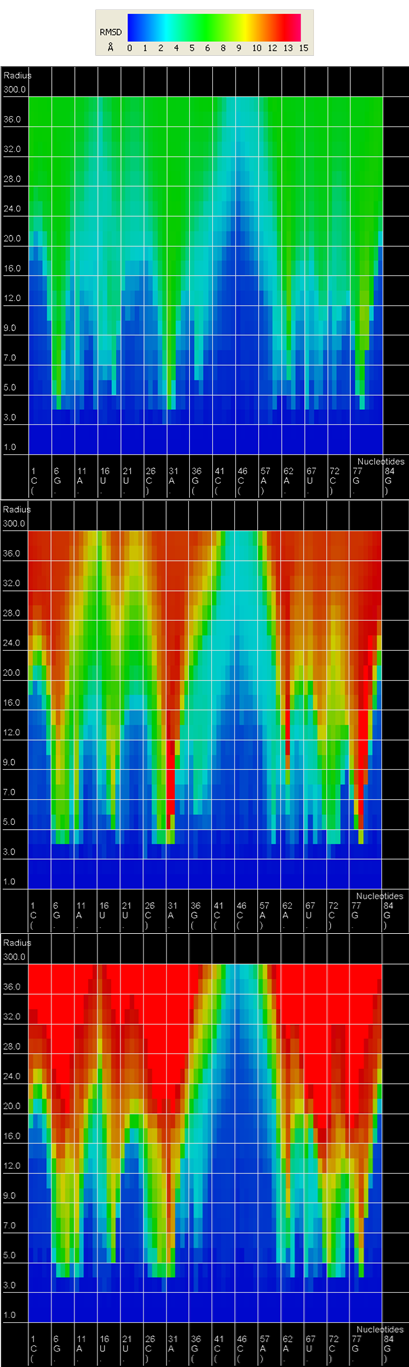
Figure 3. 2D map plot - each map corresponds to one of the analyzed models; X-axis represents the order of nucleotides in the sequence, Y-axis represents the sphere radius, color of the cell represents the RMSD value, following the scale presented at the bottom (blue – low RMSD, red – high RMSD).
3D plot
An example of a 3D plot is presented in Figure 4. The X-axis represents nucleotide numbers in sequential order, the Z-axis represents the radius values from the spheres radii vector defined by the user, and the Y-axis represents RMSD. The value of RMSD is also represented with the colored scale. Both plots (2D map plot and 3D plot) describe the accuracy of fragments of a prediction model around certain nucleotides.
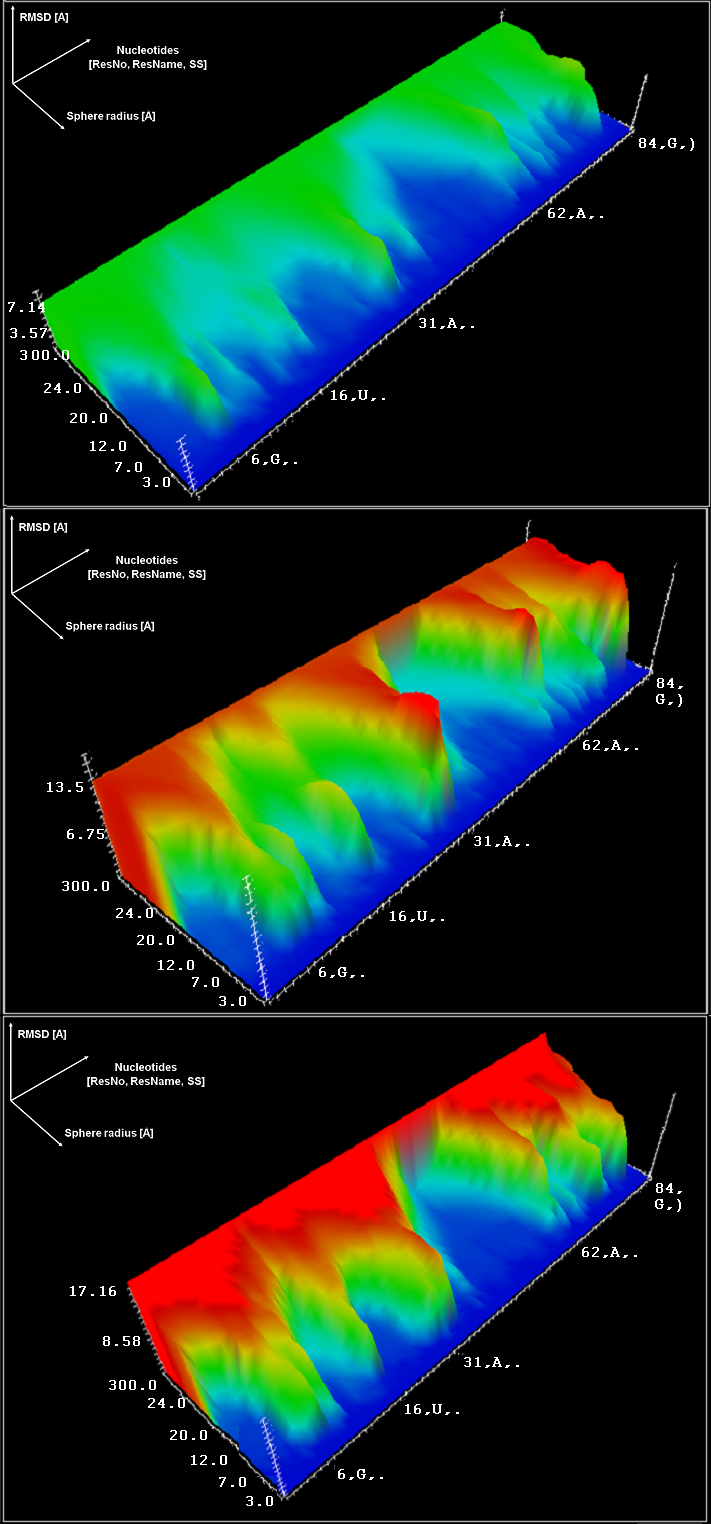
Figure 4. 3D plot – analysis of three models; X-axis represents the order of nucleotides, Y-axis represents sphere radius, Z-axis represents RMSD.
Cutoff plot
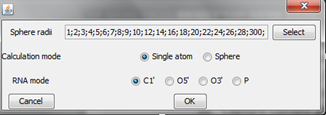
An example of a Cutoff plot is presented in Figure 5. Cutoff plot shows how accurate is the prediction of a particular model from a local point of view or, in other words, which part of the model structure is predicted correctly. The calculation is performed based on the fixed precision value (cutoff) for each sphere radius value, defined by the user in spheres radii vector. As a result, the user receives information about the atoms set predicted below cutoff (%). The value of cutoff can be changed interactively by the user.
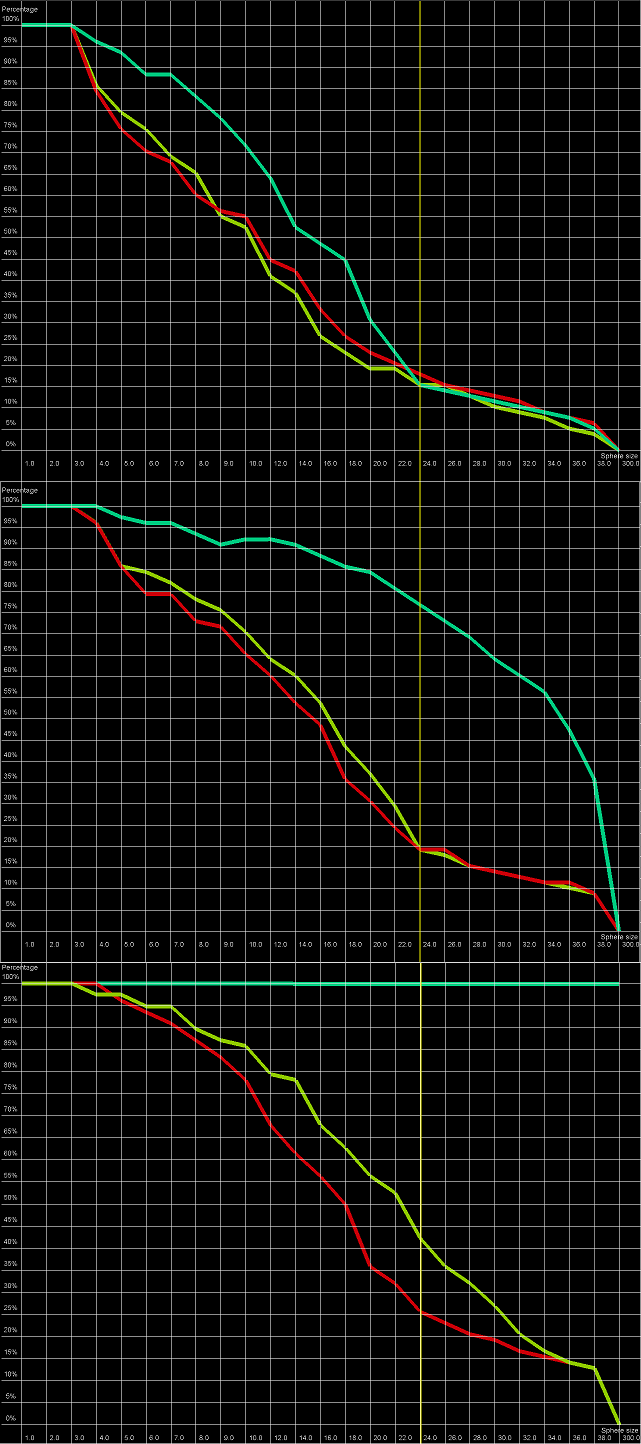
Figure 5. Cutoff plot presents a percentage of the number of atoms sets included in spheres with fixed radius for each considered model, which are below a selected precision value. One line corresponds to one model. X-axis corresponds to sphere value, Y axis corresponds to percentage value. On the picture above one can see plots for precision values (from top to the bottom: 4 Å, 7 Å and 10 Å) for radius of the sphere equal to 24 Å (different colors correspond to different models).